Android push notifications explained: Setup, permissions & best practices
With Android powering over 80% of the global mobile market, Android push notifications remain one of the most effective ways to reach, engage, and retain users.
This guide is created for marketers and app teams who want to understand how to send push notifications on Android. We’ll explain push notification Android setup, explain the latest Android notification changes, and share best practices to help you improve Android notification engagement.
Android vs iOS push notifications: key differences
Both Android and iOS provide robust push notification systems, but they differ in how messages are delivered, displayed, and managed. Understanding these differences helps marketers tailor campaigns for maximum reach, engagement, and user satisfaction on each platform.
| Aspect | Android | iOS |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery system | Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) — Google’s service that delivers notifications across Android devices. | Apple Push Notification Service (APNs) — Apple’s secure cloud gateway for iOS, iPadOS, and macOS. |
| Opt-in model | Explicit user consent required from Android 13+; automatic before Android 13. | Explicit user opt-in required on all versions. |
| Average opt-in rate (according to Puswoosh’s study) | ~75% | ~56% |
| Average CTR (according to Puswoosh’s study) | 2.75% | 1.71% |
| Notification channels/importance | Allows user-level control over message types and importance. | Managed by iOS categories; priority defined by system logic. |
| Rich media support | Images ≤10 MB, GIFs, videos ≤50 MB. Highly customizable. | Images, GIFs, and videos ≤2 MB. Strict size limits for speed and consistency. |
| Summary/grouping | Android automatically groups notifications from the same app; can be customized by the developer. | iOS uses Notification Summary and app-defined grouping. |
| Live updates/real-time widgets | Android 16 introduced “Live Updates” API for real-time delivery tracking and progress bars. | iOS supports Live Activities since iOS 16 for similar experiences. |
💡 Key takeaways:
- Reach vs engagement: Android offers broader reach and higher opt-in rates, while iOS drives slightly higher engagement per message.
- Design flexibility: Android notifications allow more creativity and interactivity — ideal for using rich push notifications on Android.
- Permission shift: With Android 13+ permission changes, app teams should now approach opt-in as a marketing strategy, not a technical step — explaining value, timing prompts correctly, and maintaining relevance are just as crucial on Android as on iOS.
What are Android push notifications?
Android push notifications are short, real-time messages sent directly to a user’s device to inform, remind, or prompt action — even when the app isn’t open. They help brands stay connected with their audience by delivering timely updates, personalized offers, or important alerts directly to the lock screen or notification tray.

With the right Android notification marketing strategy, push messages can help to increase engagement, boost retention, and drive conversions by reactivating users at key moments in their lifecycle.
How to send push notifications on Android (setup explained)
To send push notifications on Android, apps use Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) — Google’s platform that securely delivers messages between your app server and users’ devices.
Here is how the process of Android push notification delivery works, step-by-step:
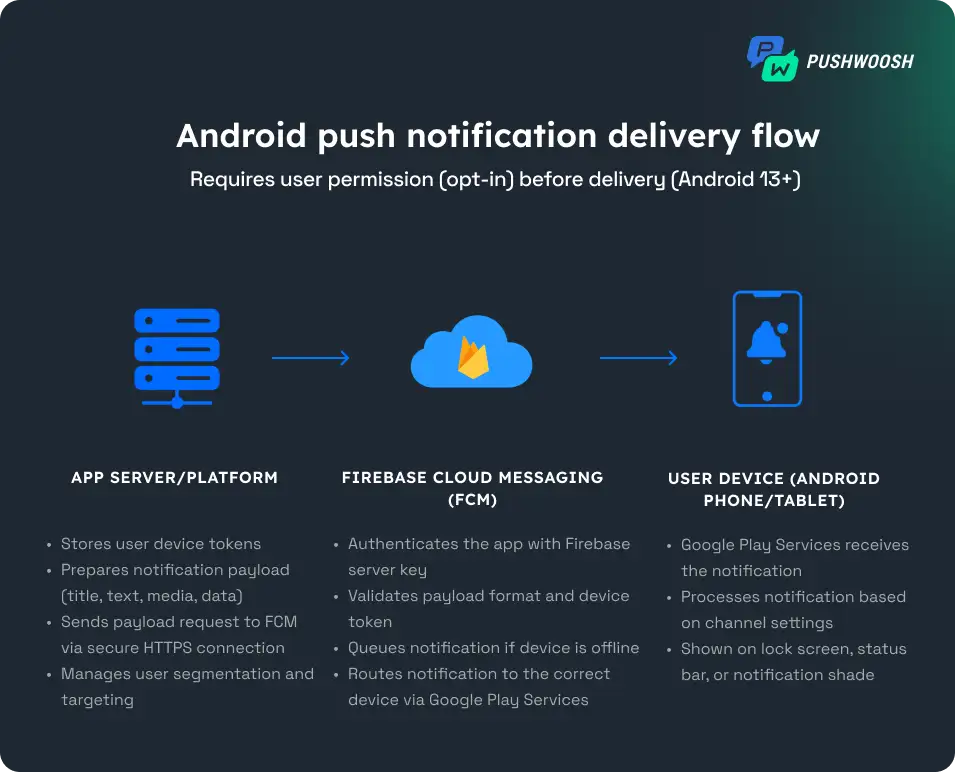
- User permission: When a user installs your app, they’re asked whether they want to receive notifications (Android 13 and later). Without opt-in, the app cannot send notifications to a user.
- Device token generation: Once the user allows notifications, the app registers with FCM to generate a unique registration token (FCM token) — an identifier that ensures each message reaches the right user and device.
- App server preparation: Your app server (or engagement platform) stores these tokens and prepares the notification payload — a JSON packet of data containing the title, message, media, custom data, and delivery parameters.
- Sending via FCM: The server sends the payload to FCM with authentication credentials, which validates it and queues the notification for delivery.
- Delivery to the user device: FCM delivers the notification through Google Play Services. The message appears on the lock screen, status bar, or as a heads-up alert, depending on user settings and device model.
Android push notification setup
To start sending Android push notifications, first you need to configure your app and connect it with FCM. Here is how to do it:
- Create a Firebase project in the Firebase Console.
- Add your Android app to the project by entering your package name, then download the google-services.json file and place it in your app’s directory.
- Add the Firebase SDK to your project by including Firebase dependencies in your build.gradle files and syncing your project.
- Implement Firebase Messaging Service in your app code to handle incoming notifications and retrieve the device FCM token.
- Configure notification channels (required for Android 8.0+) and request notification permission (required for Android 13+).
- Set up your app server to send notifications to FCM using your Server Key or service account credentials
- Test your first notification through the Firebase Console to ensure delivery works correctly.
What’s new in Android notifications (2025)
Android continues to evolve its notification experience, giving users more control over what they receive and when they see it. Understanding these updates helps app marketers fine-tune their Android push notification strategies for stronger engagement and higher delivery performance.
Android push notification permissions: What changed in Android 13 and 14
Before Android 13, push notifications were enabled by default. Once users installed your app, they automatically began receiving notifications unless they manually disabled them in settings. This broad reach allowed for mass communication but often led to notification fatigue and declining engagement over time.
The introduction of Android 13 marked a major shift in how push notifications work.
For the first time, Android apps must request explicit user permission to send notifications, aligning Android’s model closer to iOS and making the opt-in strategy more important than ever.
📊 How it impacted opt-in rates:
According to Pushwoosh’s research, opt-in rates dropped across most app categories after Android 13, but the impact varied by industry.
For example, Gaming apps lost nearly a third of their opted-in users, while finance and transportation apps saw the smallest decline, thanks to the critical nature of their notifications.

Even with this drop, the average Android 13 opt-in rate still outperforms iOS, proving that context and timing drive user consent.
Here’s a snapshot of 2025 median opt-in rates across major industries:
| Industry | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| Banking | 74.62% | 75.79% |
| Business | 79.87% | 90.07% |
| E-commerce & retail | 52.78% | 75.27% |
| Fintech | 69.64% | 83.84% |
| Media & entertainment | 55.93% | 76.68% |
| Travel & transportation | 60.48% | 84.75% |
| Games (action) | 44.17% | 74.68% |
| Health & fitness | 53.98% | 85.28% |
With Android 14, Google introduced even more granular permission management. Users can now adjust notification preferences by importance level (e.g., “High,” “Default,” or “Silent”) and by notification channel type.
Notification cooldown & cross-device notifications (Android 15+)
Android 15 adds a new Notification Cooldown feature that gradually lowers notification volume and vibration intensity when a user receives multiple messages from the same app within a short time period. This cooldown lasts for about 1–2 minutes, after which the notification volume automatically returns to normal.
Also, push notifications can now sync across multiple Android devices, including smartphones, tablets, and ChromeOS. Users can see the same notification wherever they’re active, ensuring consistency and visibility across screens.
These recent Android notifications updates mean your timing strategy matters more than ever.
Android push notification best practices to increase opt-in rates & keep users engaged
Now that we’ve reviewed the key Android updates, let’s explore the best practices marketers should follow to align with these changes and boost engagement.
✅ Ask for opt-in at the right moment and explain the value
Avoid showing the opt-in prompt immediately after install.
Request permission after a meaningful user action (such as completing onboarding or viewing a product) and show an in-app message/screen explaining the benefits of notifications.
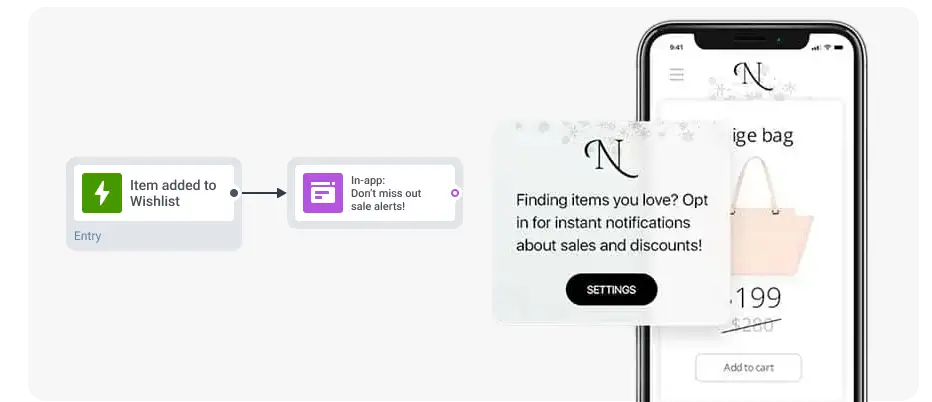
This strategy can increase approval chances.
✅ Prioritize relevance and personalize every message
Since Android’s system automatically prioritizes notifications that match a user’s real-time context and behavior, leverage triggers like “Added to cart,” “Product viewed”, “Order placed,” or “App inactivity > 14 days” to deliver timely, meaningful updates that users are more likely to interact with.
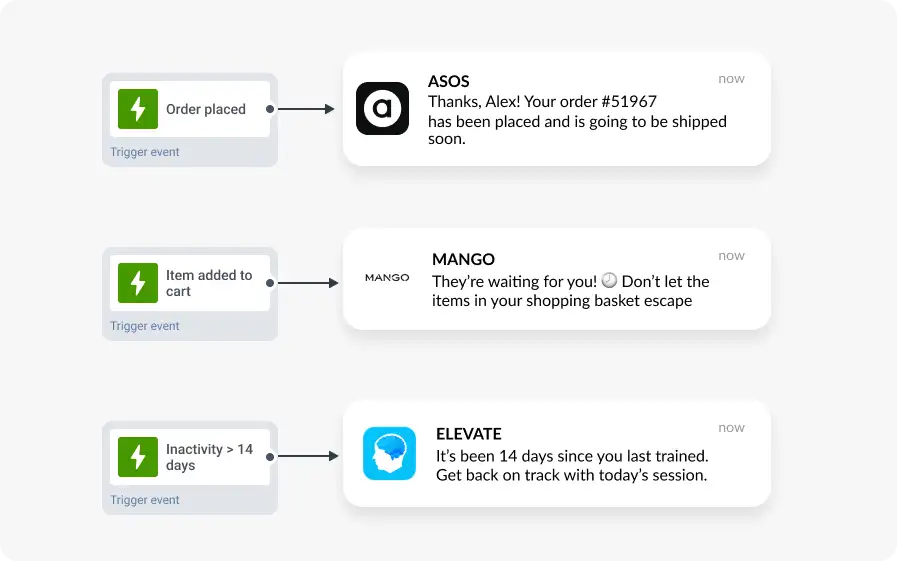
To personalize the message copy, use Dynamic content to automatically insert a user’s name, favorite product category, or other relevant info, ensuring every recipient gets a message that feels like it was written just for them.
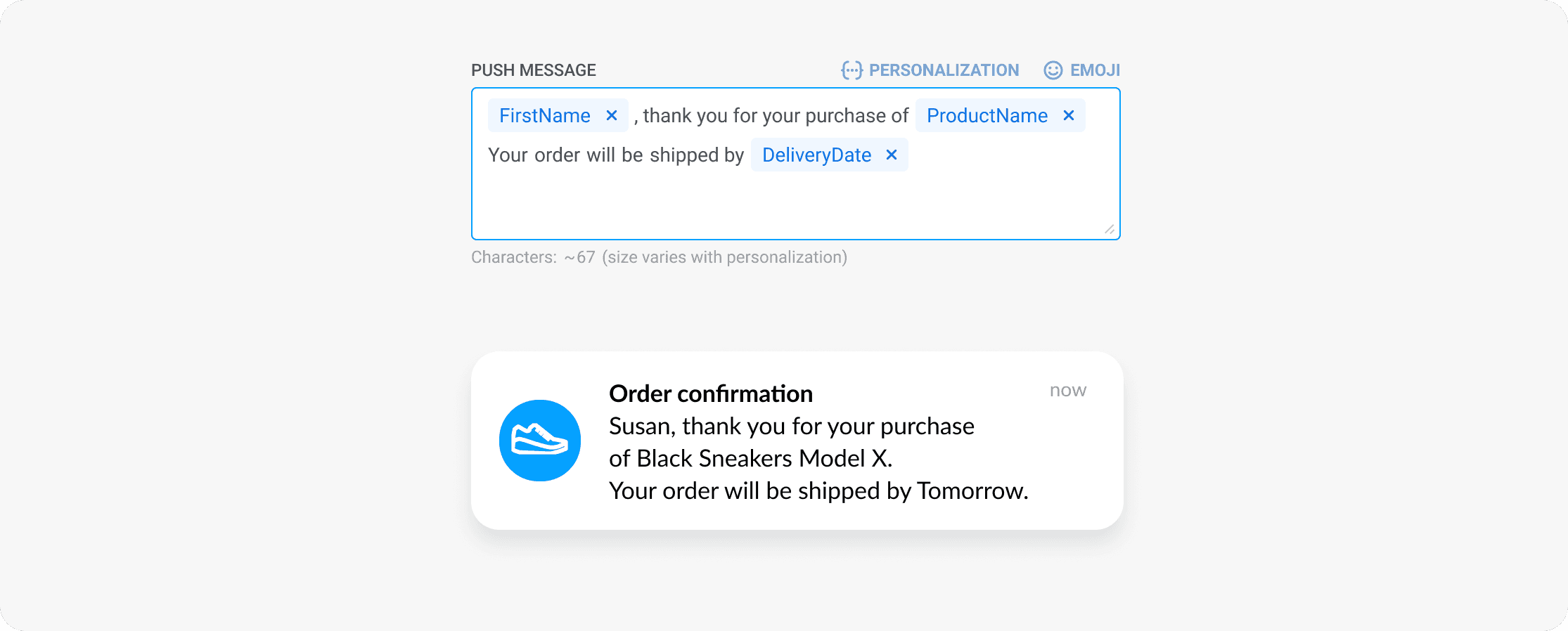
✅ Automate delivery at the perfect time
Avoid sending messages to your audience in a single blast. This can significantly decrease push notification engagement, reduce visibility under the latest Android system updates, and make users opt out.
Instead, let automation handle it. Schedule push notifications to go out exactly when users are most likely to engage:
- Set a Silence period to prevent nighttime delivery and automatically pause pushes during users’ sleep hours.
- Master Pushwoosh’s Best time to send feature to deliver each message at the user’s individual peak activity window, ensuring up to 50% higher open rates and engagement.
✅ Test and optimize
Even with automation and perfect timing, consistent testing is key to growth.
Use A/B/n tests to experiment with different versions of your notifications (from title and copy to visuals, CTAs, and send time) and identify what drives the best engagement.
Track performance metrics, such as opt-in and opt-out rates, CTR, and conversions, to understand what resonates with your audience. Over time, these small optimizations compound into significantly stronger campaign performance.
Android push notification design essentials
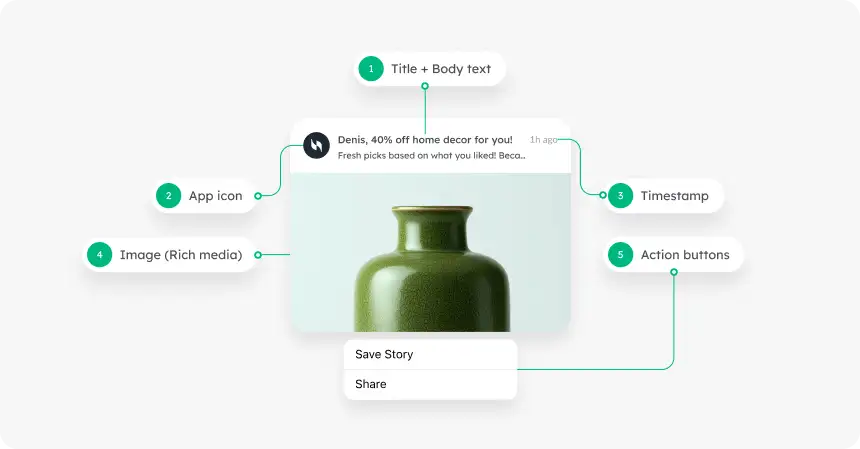
Character limits
Keep messages short and actionable.
- Title: 25–50 characters
- Message body: up to 150 characters (first 40 are most visible)
Rich push notifications on Android
Recent Android versions support larger visuals along with carousel-style previews and interactive action buttons.
Compared to iOS, Android offers greater flexibility and screen presence, giving marketers the opportunity to make their pushes more creative, dynamic, and engaging.
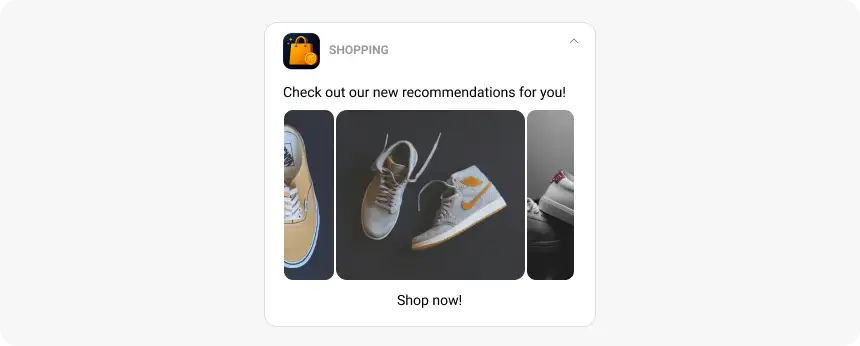
- Supported formats: JPEG, PNG, GIF, MP4, MP3, WAV
- Size limits: ≤10 MB for images or GIFs, ≤50 MB for video/audio
Use rich media to capture attention, but always test loading speed and performance to maintain a smooth user experience across Android devices.
Notification channels
Create clear notification channels (e.g., “Promotions,” “Updates,” “Reminders”) so users can easily manage their preferences.
Don’t overload users — stick to 3–5 channels for clarity and consistency.
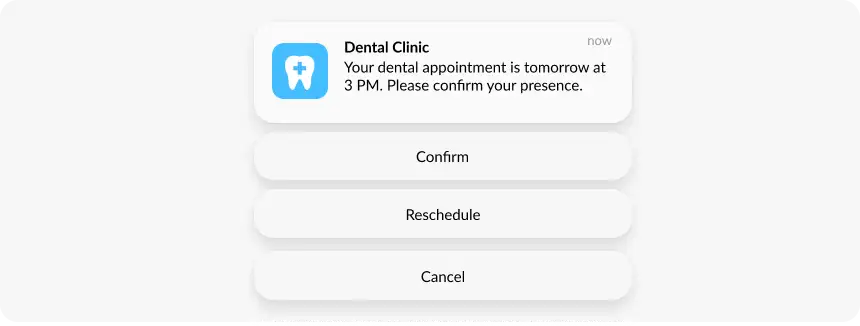
CTAs and action buttons
Add up to three action buttons to your notification (e.g., “Shop Now,” “Track Order,” “Read More”).
Keep them short (1–2 words) and clear to drive instant interaction.
Android push notification benchmarks (2025 data)
To help you measure and improve your Android campaigns, Pushwoosh analyzed data from over 600 apps across major industries. The table below shows the average Android push notification opt-in and click-through rates (CTR) based on Pushwoosh benchmarks.
These metrics will help you understand how your app performs compared to the industry standard and identify where you can optimize.
| Industry | Android push notification opt-in rate | Android push notification CTR |
|---|---|---|
| E-commerce & retail | 75.28% | 3.78% |
| Fintech | 83.85% | 2.84% |
| Action games | 74.68% | 0.82% |
| Hypercasual games | 69.03% | 1.05% |
| Media & entertainment | 76.68% | 1.69% |
| News | 68.00% | 2.63% |
📊 All-industries average: Opt-in rate: 75.24%, CTR: 2.75%
Pushwoosh — the best Android push notification service
Automate high-performing Android push notifications with Pushwoosh, an all-in-one customer engagement platform that helps you send, personalize, and analyze campaigns effortlessly.
✅ Omnichannel: Manage iOS and Android push notifications, web notifications, email, SMS, and WhatsApp — all from one place.
✅ Marketer-friendly tools: Use a visual, no-code Customer Journey Builder to design automated flows with triggers, delays, and personalization.
✅ Best-in-class deliverability: Fully compliant with the latest Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) and Android updates for reliable message delivery.
✅ Advanced segmentation: Target users based on behavior, tags, or RF(M) parameters for precise, relevant communication.
✅ Real-time analytics: Track CTR, conversions, opt-in rates, and retention uplift to measure your true impact.
✅ AI optimization: With Pushwoosh AI Assistant, automate message creation, multilingual localization, segmentation, and campaign performance insights.
FAQ
What changed in Android 13 and 14 notification permissions?
Starting with Android 13, apps must explicitly request user permission to send notifications — they’re no longer enabled by default. Android 14 expanded user control even further, allowing preferences by importance level (High, Default, Silent) and notification channel type (e.g., Promotions, Reminders).
What is Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM)?
Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM) is Google’s push notification service that delivers messages to Android devices. It authenticates your app, handles message routing, and supports advanced options like data-only pushes, topics, and device group messaging.
Pushwoosh integrates directly with FCM to ensure high deliverability and automation across Android campaigns.
What is the difference between FCM and APNs?
- FCM (Firebase Cloud Messaging) delivers push notifications to Android devices.
- APNs (Apple Push Notification service) delivers notifications to iOS devices.
Both serve similar functions but differ in payload limits, configuration steps, and delivery logic.
Pushwoosh supports both, enabling unified cross-platform messaging.
What are rich push notifications on Android?
Rich push notifications include media like images, GIFs, or short videos. Android supports larger file sizes (up to 10 MB for images/GIFs and 50 MB for videos/audio) and interactive layouts, allowing more creative and engaging campaigns than iOS.




.webp)
